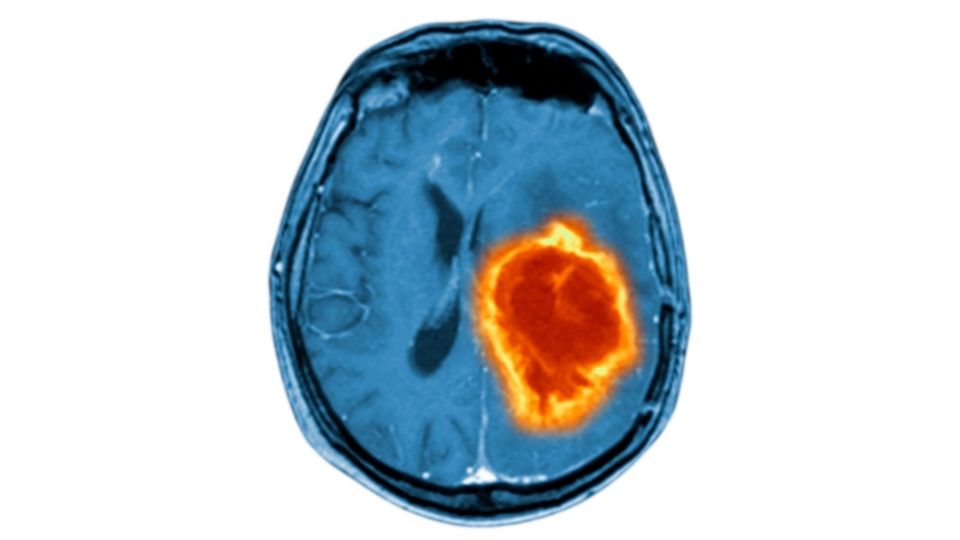
- A brain tumor is an abnormal collection of cells in the brain, in which the cells divide and grow uncontrollably leading to an abnormal mass of tissue
- The 2 main groups of brain tumors are Primary and Metastatic
- The presentation of brain tumors depends on the areas of brain involved. They can present with:
- Headache
- Seizures
- Focal neurologic deficit as a result of
- Weakness
- Numbness
- Speech difficulties
- Visual deficits
- Imbalance
- Personality changes
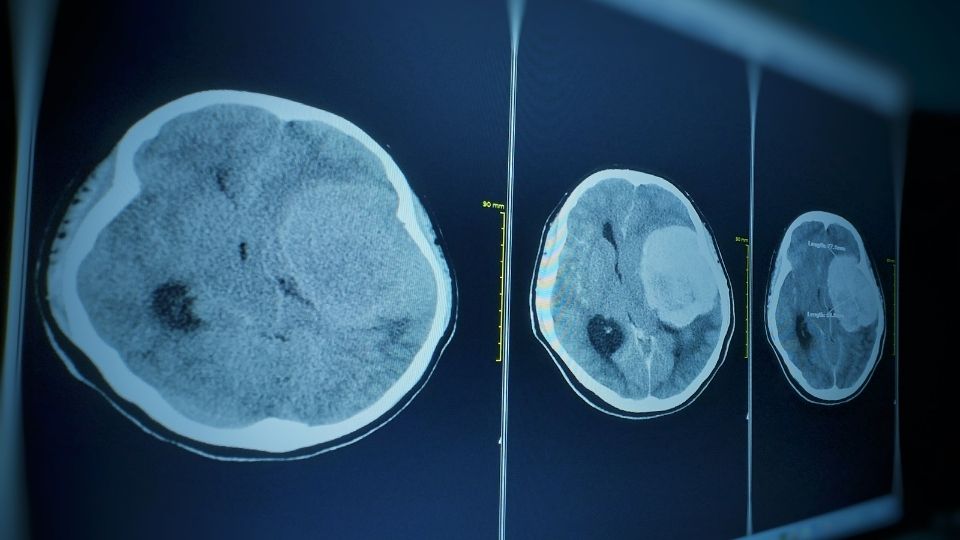
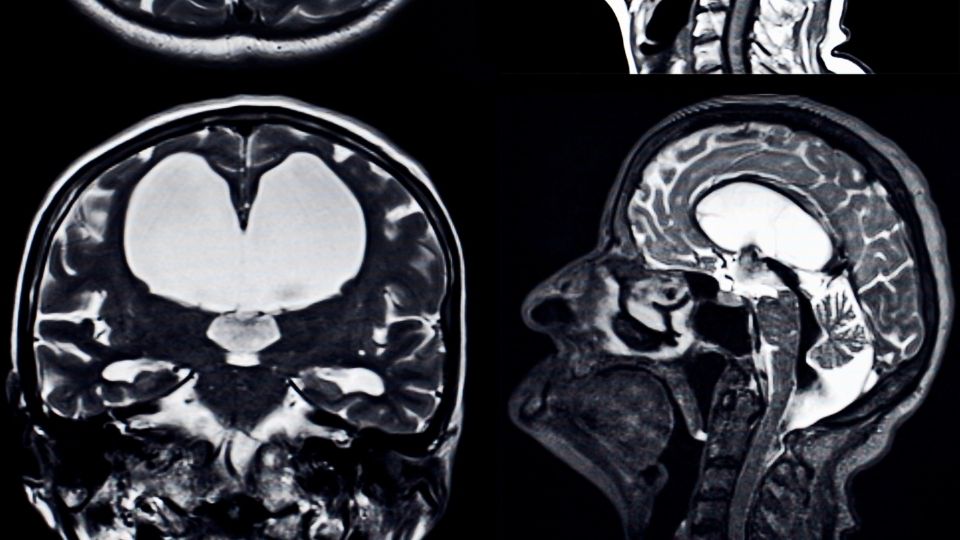
- Diagnosis involves cranial imaging
- Head CT
- Typically the first imaging test to be done
- Able to detect swelling in the brain but the resolution is often not high enough to assess the exact location, size and shape of the tumor
- Administration of contrast helps to define the tumor
- Brain MRI
- Typical imaging modality for brain tumors
- Administration of contrast helps to define the tumors better
- Typically aggressive tumors enhance after contrast
- Allows visualization of the tumor in 3 dimensions
- Head CT
Brain Tumors